Tekton
What is Tekton?
Tekton is a powerful, cloud-native, open-source framework for creating CI/CD systems. As a Kubernetes-native solution, Tekton enables you to build, test, and deploy across cloud providers and on-premises systems by abstracting away the underlying details. Born as an open-source project under the umbrella of the Continuous Delivery Foundation (CDF), Tekton has evolved into one of the most robust and flexible CI/CD platforms available in 2025.
Tekton leverages Kubernetes Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) to define CI/CD pipeline components as code, providing a declarative approach to DevOps automation. It brings enterprise-grade features like security, compliance, observability, and multi-cloud portability to your CI/CD workflows, making it the preferred choice for organizations adopting cloud-native methodologies.
Why Choose Tekton in 2025?
Cloud-Native Architecture: Built from the ground up for Kubernetes environments
Vendor Neutral: Works across all major cloud providers (AWS, Azure, GCP) and on-premises
Supply Chain Security: Built-in support for SLSA compliance and software supply chain security
GitOps Ready: Seamless integration with GitOps workflows and ArgoCD
Enterprise Grade: Battle-tested in production by organizations like Google, IBM, Red Hat, and VMware
Key Features and Concepts (2025)
Core Components
1. Tasks The fundamental building blocks of a Tekton pipeline are tasks. Each task represents a specific unit of work, such as building code, running tests, or deploying an application. Tasks can be combined and reused across pipelines, promoting modularity and code sharing.
2. Pipelines Pipelines provide a way to orchestrate tasks in a specific order to create an end-to-end CI/CD workflow. With Tekton, you can define complex pipelines that include multiple stages, parallel execution, and conditional branching.
3. PipelineRuns and TaskRuns These are the runtime instances of Pipelines and Tasks. They represent the actual execution of your defined workflows with specific parameters and workspaces.
4. Workspaces Workspaces allow you to share files between tasks within a pipeline. They provide a mechanism for passing data and artifacts between different stages of the CI/CD workflow. Workspaces ensure isolation and reproducibility, making it easier to manage complex pipelines.
5. Parameters and Results Parameters enable dynamic configuration of tasks and pipelines at runtime, while Results allow tasks to output data that can be consumed by subsequent tasks.
New 2025 Features
Supply Chain Security (SLSA Compliance)
Built-in support for generating SLSA provenance
Signed task and pipeline execution attestations
Integration with Sigstore for keyless signing
Enhanced Security Model
Pod Security Standards enforcement
Service mesh integration (Istio, Linkerd)
RBAC templates for common use cases
Performance Improvements
Faster pipeline startup times (50% improvement over 2024)
Optimized resource scheduling
Better memory management for large pipelines
GitOps Integration
Native ArgoCD integration
Automated pipeline synchronization
Git-based pipeline definitions with auto-discovery
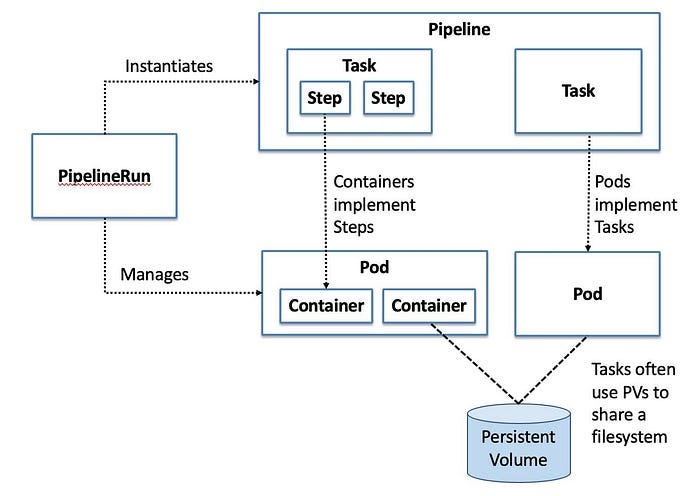
A task can consist of multiple steps, and pipeline may consist of multiple tasks. The tasks may run in parallel or in sequence
Real-World Examples (2025)
Example 1: AWS EKS CI/CD Pipeline with SLSA Compliance
This example demonstrates a complete CI/CD pipeline for deploying to AWS EKS with supply chain security features.
Example 2: Azure AKS Multi-Environment Pipeline
This pipeline demonstrates deploying to multiple Azure environments with approval gates.
Example 3: GCP Cloud Run Serverless Pipeline
This example shows a serverless deployment pipeline for Google Cloud Run with automated scaling.
Example 4: Multi-Cloud GitOps Pipeline
This advanced example demonstrates a GitOps pipeline that can deploy to multiple cloud providers.
Pipeline Triggers and EventListeners (2025)
Modern webhook configuration for GitLab, GitHub, and Azure DevOps:
These examples showcase:
SLSA Compliance: Supply chain security with image signing and provenance generation
Multi-Environment Deployments: Proper staging with approval gates
Serverless Deployments: Cloud Run with auto-scaling configuration
GitOps Integration: Configuration management with automated updates
Modern Webhooks: Advanced event filtering and processing
Security Scanning: Container vulnerability assessments
Multi-Cloud Support: Unified pipelines across cloud providers
Installation Guide (2025)
Prerequisites
Kubernetes cluster 1.28+ (recommended: 1.29 or later)
kubectl configured to access your cluster
Cluster-admin permissions
At least 2GB of available memory and 2 CPU cores
Installing Tekton Pipelines (v0.55.0+)
To install Tekton Pipelines on a Kubernetes cluster:
Install the latest stable release:
For specific versions or alternative installations:
Monitor the installation:
When all components show 1/1 under the READY column, the installation is complete.
Installing Tekton Triggers (v0.26.0+)
Install Tekton Triggers for webhook and event-driven pipelines:
Installing Tekton Dashboard (v0.40.0+)
Install the web-based dashboard:
Installing Tekton CLI (tkn) v0.35.0+
Installation on Different Operating Systems
Linux Installation
WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) Installation
NixOS Installation
Best Practices for Tekton in 2025
Security First
Always use signed images and SLSA provenance
Implement proper RBAC and security contexts
Regularly scan for vulnerabilities
Resource Management
Use resource quotas and limits
Implement proper workspace management
Monitor pipeline performance
GitOps Integration
Store pipeline definitions in Git
Use automated synchronization
Implement proper branching strategies
Observability
Enable comprehensive logging
Use distributed tracing
Implement monitoring and alerting
Getting Started with Your First Pipeline
DevOps Joke: Why did the developer choose Tekton over other CI/CD tools? Because they wanted their pipelines to be as declarative as their love for Kubernetes - and just like their relationship status, everything had to be defined in YAML! 😄
At least with Tekton, when your pipeline fails, you can blame it on the cluster and not your code... most of the time!
Last updated