Status in Pods
Pod in ContainerCreating Status
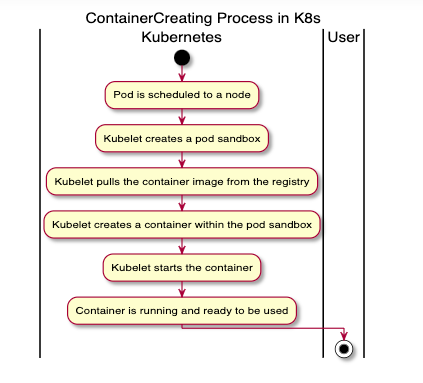
In K8s, when a pod status shows “ContainerCreating”, it means that the pod has been scheduled on a node (the decision has been made regarding which node the pod should run on), and the kubelet on that node is in the process of creating the containers for that pod.
During this phase, the following actions are performed:
Pulling the required Docker images onto the node (if they are not already available locally).
Creating the containers from these images.
Starting the containers.
If everything goes as expected, the pod status transitions from “ContainerCreating” to “Running” once all of the containers within the pod are up and running.
Common Causes
If a pod is stuck in ContainerCreating status for a long time, it generally indicates that there’s an issue preventing the containers from being successfully created. Some of the common reasons include:
Image Pull Issues: This is one of the most common issues. It could be that the specified image doesn’t exist, the image name is misspelled, or there’s a network issue preventing the image from being pulled.
Insufficient Resources: If the node doesn’t have enough CPU or memory resources available to run the containers, then the pod will not be able to move past the “ContainerCreating” status.
Network Issues: If there’s a network issue, such as a problem with the CNI (Container Network Interface) plugin, it might prevent the containers from being created.
Security Context Issues: If the security context for the pod or container is not properly configured (for example, the pod is trying to run as a specific user that doesn’t exist), it can prevent the container from starting.
Docker or Runtime Issues: If there are issues with the Docker daemon or container runtime, it could prevent the containers from being created.
Issues with Persistent Volumes: If the pod is dependent on a Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) and that PVC is not available or can’t be mounted for some reason, the pod will remain in the “ContainerCreating” state.
How to Troubleshoot
Image Pull Issues
You can use the kubectl describe pod <pod-name> command to check the events of the pod.
Look for “Failed to pull image” or “ImagePullBackOff” events. These indicate issues with pulling the container image. If you see authentication errors, check your imagePullSecrets and registry credentials.
Real-life example:
Insufficient Resources
Use the kubectl describe node <node-name> command to check the resources on your node.
Check the Allocatable and Capacity sections, and look for events about resource pressure (e.g., OutOfcpu, OutOfmemory).
Real-life example:
Issues with Persistent Volumes
You can check Pod status using kubectl:
Look for errors like:
Then check the PVC status:
If the STATUS of a PVC is not “Bound”, there might be issues with storage provisioning. For cloud providers, check your storage class and cloud disk quotas.
Real-life example:
Network Issues
Network issues can be a bit harder to diagnose. You can check the logs of your CNI plugin (which depends on the specific CNI you are using). For example, if you’re using Calico, you can check the logs of the Calico pods:
For AWS EKS, Azure AKS, or GCP GKE, check the cloud provider’s CNI documentation and ensure your VPC/subnet/network policies allow pod networking.
Security Context Issues
Check the security context of your Pod using the kubectl get pod <pod-name> -o yaml command.
Look for fields like runAsUser, fsGroup, or privileged. Ensure the user/group exists in the container image and that the node allows the requested privileges.
Docker or Runtime Issues
Check the logs on your node. The way to do this depends on your node’s operating system and your container runtime. For Docker on a system using systemd, you can use:
For containerd:
On managed Kubernetes (EKS, AKS, GKE), use the cloud provider’s node troubleshooting tools or review logs in the cloud console.
Additional Troubleshooting Tips
Use
kubectl get events --sort-by=.metadata.creationTimestampto see recent cluster events.Use
kubectl logs <pod> -c <init-container>to check init container logs if present.For multi-cloud: Check IAM roles, disk quotas, and network security groups in AWS, Azure, or GCP.
Use kubectl-debug or stern for advanced debugging.
References
Tip: Always check
kubectl describe pod, node status, PVCs, and CNI logs. For cloud clusters, use provider-specific troubleshooting docs and dashboards.
Conclusion

Last updated